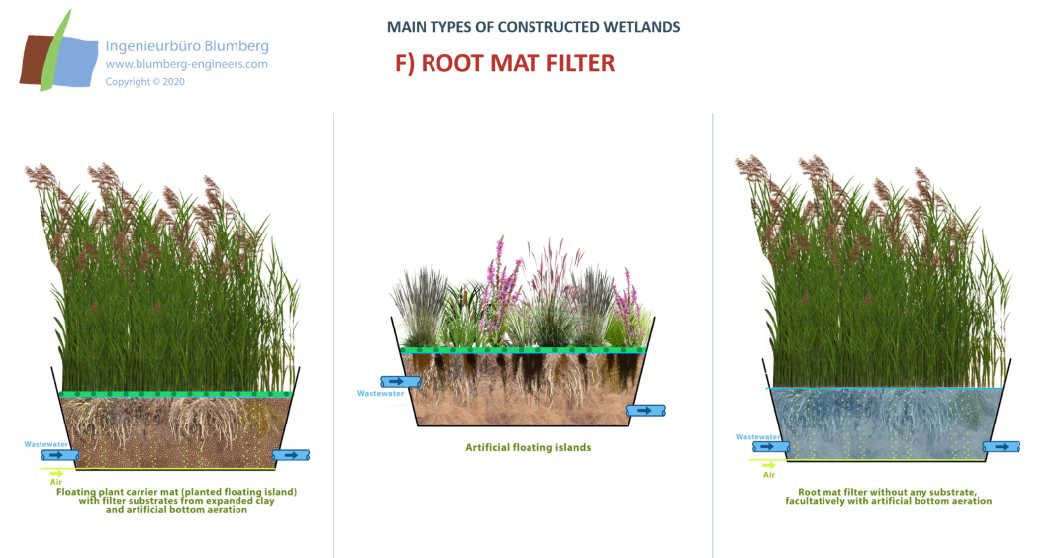
Reed bed treatment systems
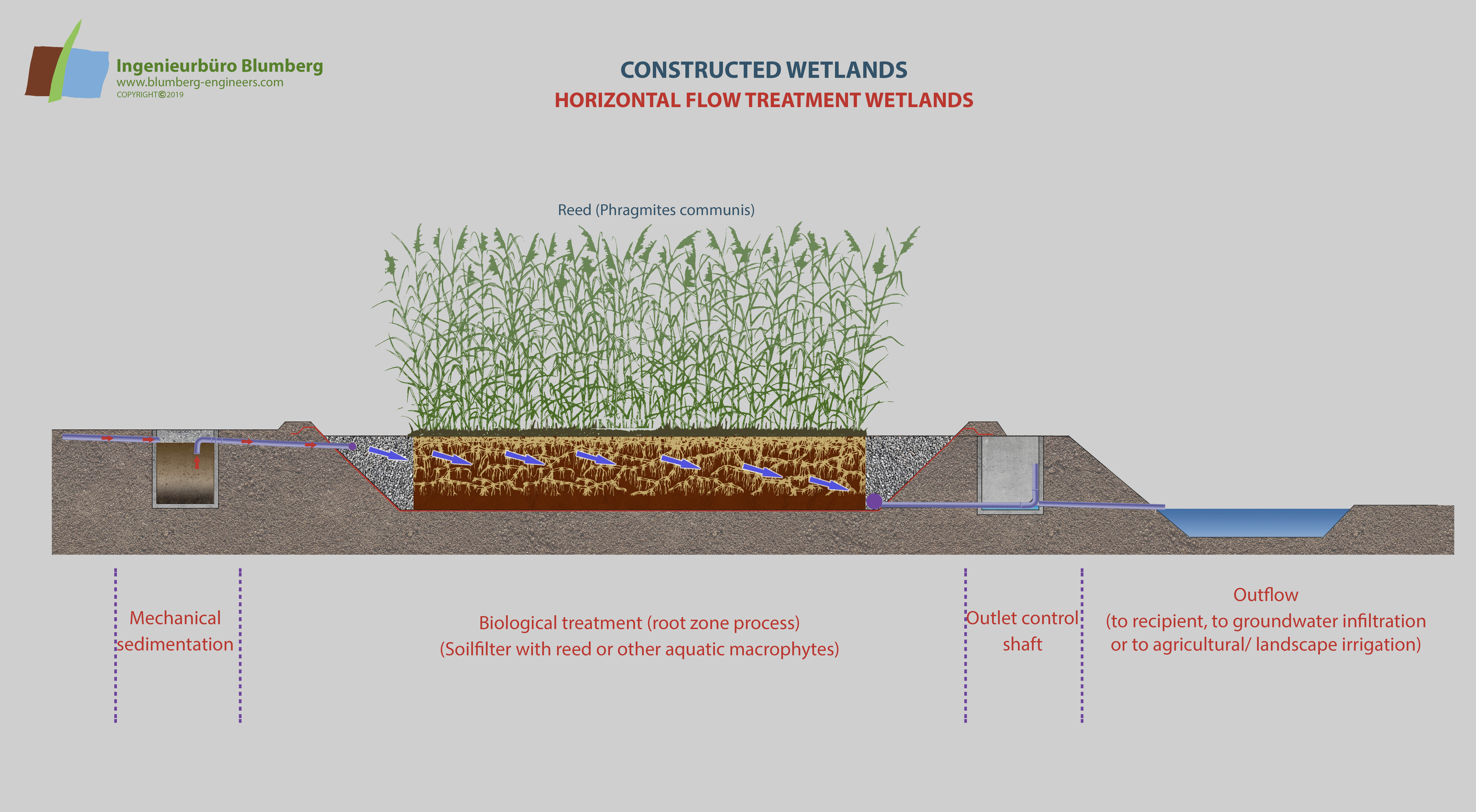
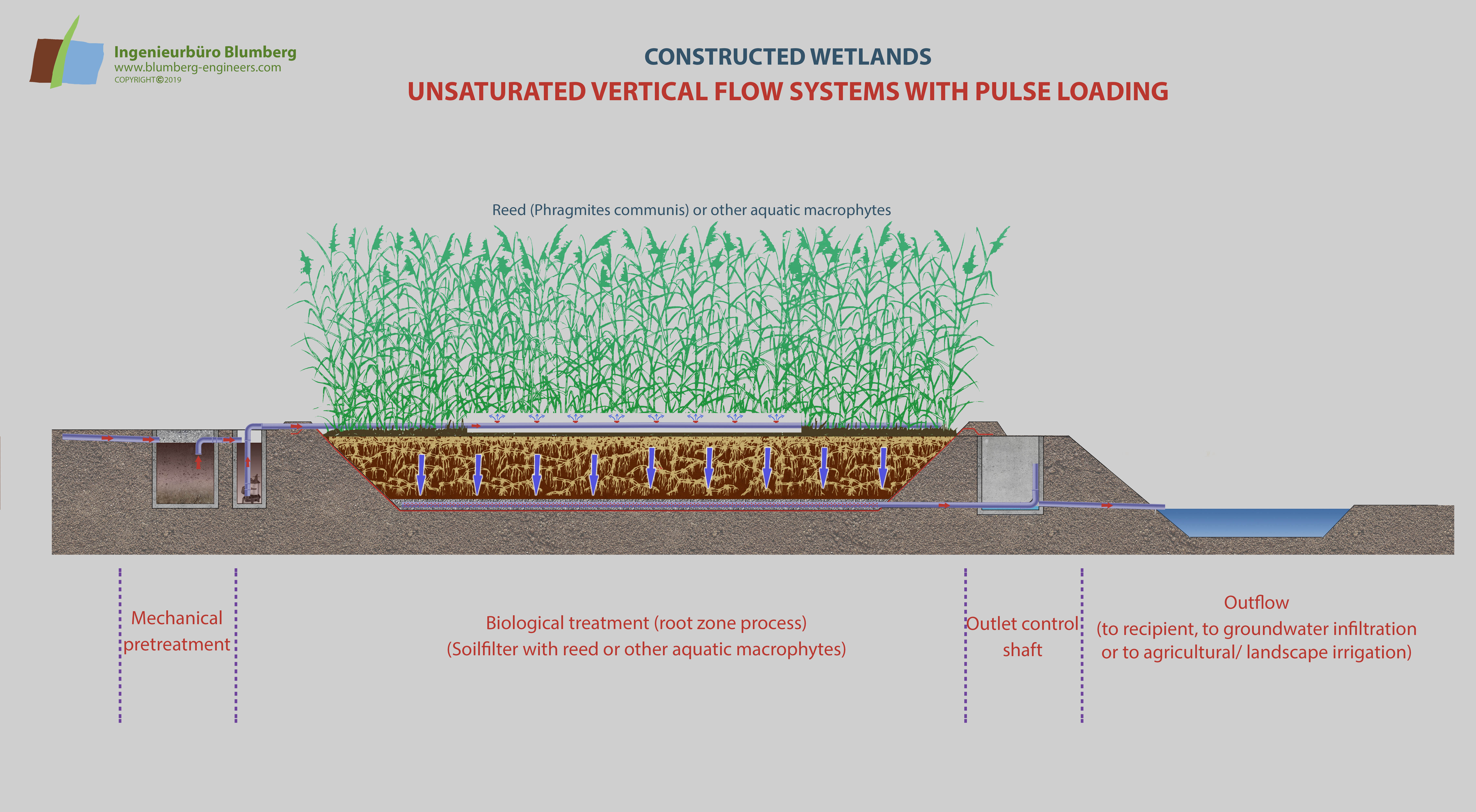
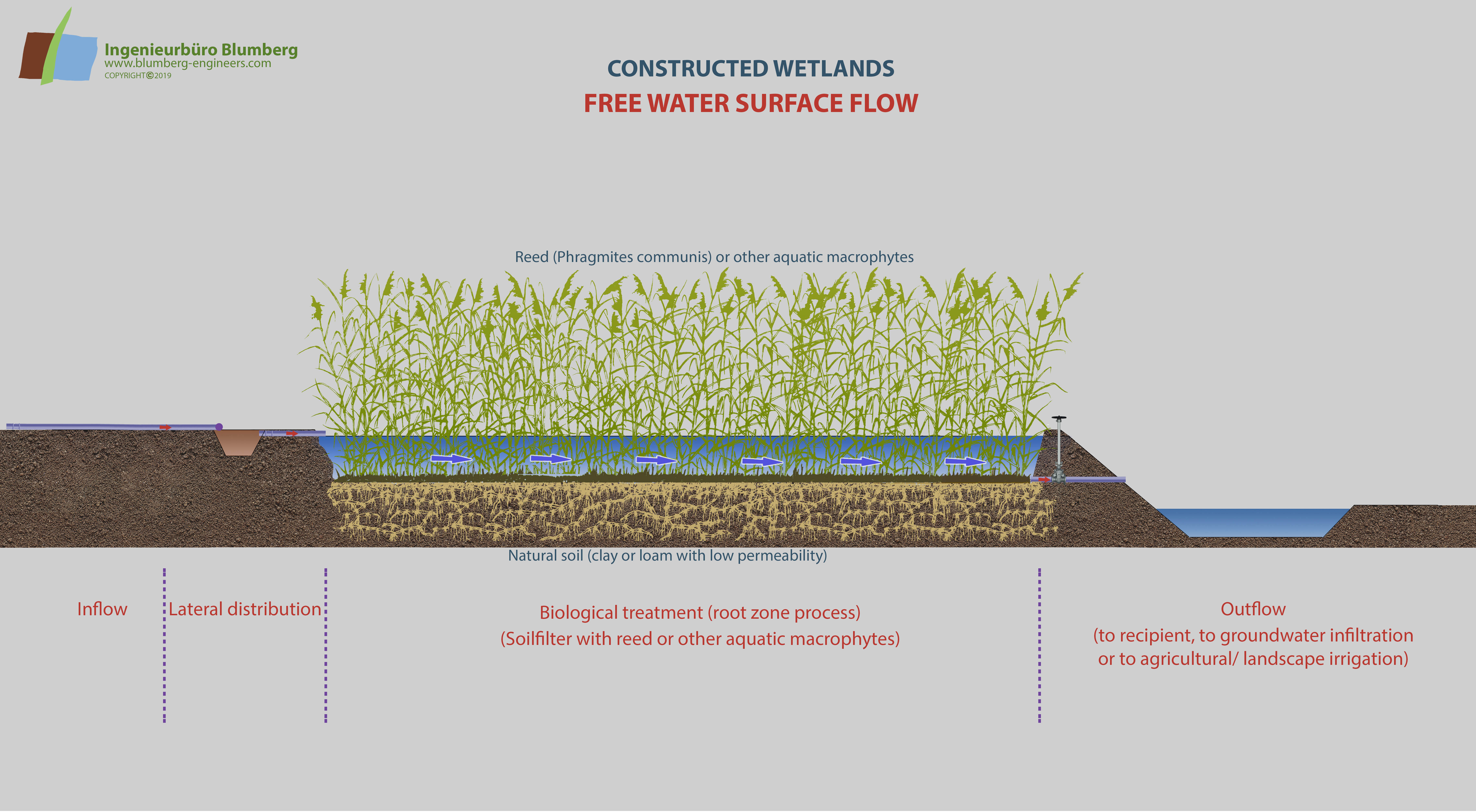
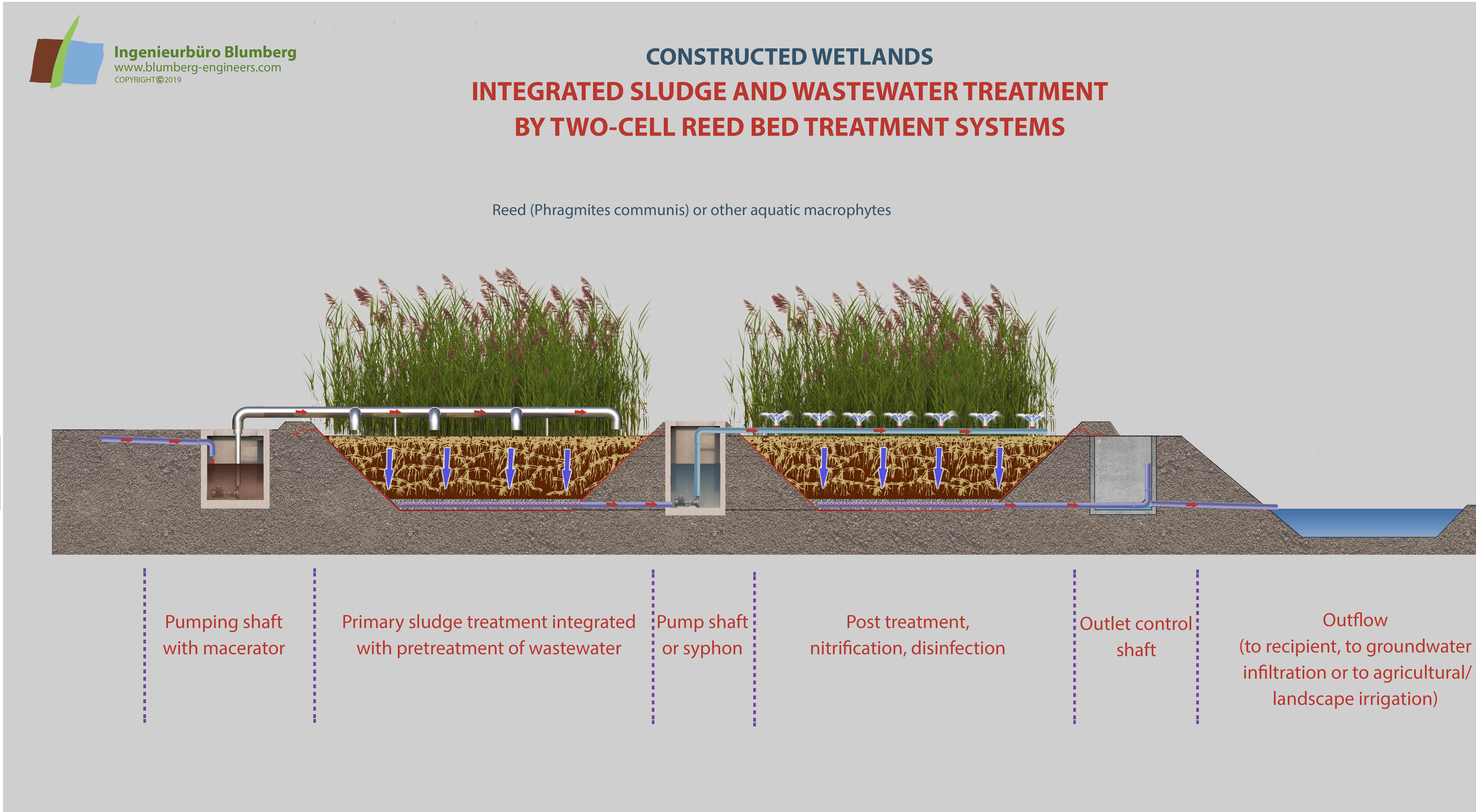
The reed bed treatment system combines aerobic and anaerobic decomposition processes in a soil or substratum layer. The system can be used as the main step for wastewater treatment or as a downstream step for further purification. The polyethylene lined and basins are filled with soil, sand or gravel and are planted with domestic helophytes like Phragmites communis, Typha latifolia, Typha angustifolia or other aquatic macrophytes.
The wastewater percolates the filter substrate. Besides the microbial and fungal decomposition of organic matter and pollutants in the rooted substrate matrix, chemical and physical precipitation, adsorption and filter processes occur due to soil constituents like clay minerals and humus particles. This is most important for phosphate and ammonia binding. Some of the wastewater nitrogen is released out of the artificial ecosystem to the atmosphere as nitrogenous gases (denitrification).
Through intermittent loading of the reed beds a radical change of oxygen regime can be achieved. After saturating the filter with water by feeding it through the distribution system, a drainage network at the base collects the purified water. When the water runs off the pore space of the substrate is refilled with air enabling aerobic decomposition processes.